Managed Hosting vs. Cloud Hosting: A Definitive Guide for Your Business

Index
- Introduction: The Hosting Dilemma
- Deconstructing Managed Hosting: The "Done-For-You" Solution
- How Managed Hosting Works in Practice
- The Powerful Advantages of Managed Hosting
- The Inherent Disadvantages of Managed Hosting
- Demystifying Cloud Hosting: The "Build-Your-Own" Universe
- How Cloud Hosting Fundamentally Works
- The "as-a-Service" Models
- The Unmatched Advantages of Cloud Hosting
- The Significant Disadvantages of Cloud Hosting
- Blurring the Lines: The Rise of Managed Cloud Hosting
- Head-to-Head Comparison: Managed Hosting vs. Cloud Hosting
- Making the Right Choice: Which Hosting Is for You?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion: Convenience vs. Control

For any business building or scaling its online presence, the choice of a hosting solution is one of the most foundational and critical decisions to be made. This choice is the digital bedrock upon which your website, applications, and customer experiences are built. Get it right, and you have a seamless, scalable, and secure platform for growth. Get it wrong, and you could face frustrating downtime, security vulnerabilities, and crippling limitations as your business evolves.
At CodeDesign.ai, we've navigated this complex landscape with hundreds of clients, and we understand that the right hosting is the silent engine behind digital success. Two of the most prominent choices in today's market are managed hosting and cloud hosting. While both provide the essential service of storing your data and making it accessible to the world, they approach this task from fundamentally different philosophies. They differ significantly in architecture, performance, scalability, cost, and the level of management required from you.
Think of it like this: choosing managed hosting is like leasing a high-end, fully-serviced office. The building management handles security, maintenance, and utilities. You simply move in and focus on your work. Cloud hosting, on the other hand, is like being given access to a vast, modular construction kit. You have an incredible array of tools to build the exact structure you need, but you are the architect and the construction crew.
This guide will serve as your blueprint. We'll dismantle each hosting model, explore its inner workings, weigh its advantages and disadvantages, and provide clear, actionable insights to help you determine which one is the perfect fit for your business.
Deconstructing Managed Hosting: The "Done-For-You" Solution

Managed hosting is a service model where a hosting provider leases you dedicated servers and then takes on the complete, end-to-end responsibility for managing that infrastructure. It’s an all-inclusive service designed to remove the complexities and technical burdens of server administration from your plate.
This option is exceptionally attractive to businesses that do not have a dedicated in-house IT department, or for those who do, but prefer that their technical talent focuses on developing core business applications rather than on routine server maintenance.
How Managed Hosting Works in Practice
When you sign up for a managed hosting plan, you're not just renting server space; you're hiring a remote team of system administrators and security experts. This team's sole purpose is to ensure your server environment is secure, optimized, and running at peak performance 24/7.
- Proactive Management & Monitoring: The provider continuously monitors critical server resources like CPU usage, memory, and storage. Infrastructure monitoring tools watch for security threats and performance bottlenecks, often resolving issues before you even know they exist.
- Comprehensive Security Suite: Security is a core component. This includes configuring firewalls, performing regular malware scans, implementing intrusion detection systems, and providing robust DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) mitigation.
- Software Updates and Patching: A managed hosting provider handles the crucial task of applying security patches and software updates to the server's operating system and core applications, protecting you from known exploits.
- Performance Optimization: A key differentiator is application-specific tuning. For instance, a Managed WordPress Hosting provider will configure a server stack (e.g., NGINX, Varnish Cache, Redis) specifically to make WordPress sites fly.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Managed hosts implement automated, regular backup schedules. They not only store these backups but also have a clear process for restoring your data quickly in the event of a failure.
- Expert Technical Support: You typically get direct access to high-level support engineers who possess a deep understanding of the server environment.
The Powerful Advantages of Managed Hosting
- Peace of Mind and Focus: By outsourcing the technical complexities, you can redirect your valuable time and energy toward what you do best: running and growing your business.
- Fortress-Like Security: With a dedicated team of security professionals managing your server, your digital assets are significantly safer. This is crucial for e-commerce sites or businesses handling sensitive customer data.
- Optimized for Speed and Performance: Slow websites lose customers. Managed hosts fine-tune every aspect of the server stack, leading to faster page load times, a better user experience, and improved SEO.
- Predictable Costs: Managed hosting plans typically come with a fixed monthly or annual fee. This makes budgeting straightforward and predictable, with no surprise bills.
- Guided Scalability: As your business grows, a managed provider works with you to scale your resources. This is typically a structured process, involving a consultation and a scheduled migration to a more powerful server.
The Inherent Disadvantages of Managed Hosting
- Higher Cost: This premium, all-inclusive service comes at a premium price. You are paying not just for the hardware, but for the expertise and labor of the management team.
- Limited Flexibility and Control: The provider standardizes its environment for stability. This means you have less administrative control and may be restricted from installing certain software or making deep configuration changes.
- Dependence on Provider: Your ability to implement changes is tied to your provider's workflow and timeline. You'll have to submit a request and wait for their team to handle it.
- Resource Bottlenecks: While you can scale by upgrading plans, you are often still limited by the resources of a single server. True, instantaneous elasticity is generally not a feature.
Demystifying Cloud Hosting: The "Build-Your-Own" Universe

Cloud hosting represents a paradigm shift from the traditional single-server model. Instead of your website residing on one machine, it leverages the resources of a vast network of virtual servers. This "cloud" is designed for immense flexibility, reliability, and scalability.
Major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure dominate this space, offering a staggering array of services that go far beyond simple website hosting.
How Cloud Hosting Fundamentally Works
The core technology behind cloud hosting is virtualization. A powerful physical server is used to create and manage multiple independent virtual machines (VMs) or "instances." Each instance acts like its own self-contained server.
- On-Demand Resource Allocation: The defining feature is the ability to provision and de-provision resources in real-time. Need more computing power? Spin up ten new server instances in minutes. Campaign over? Shut them down just as quickly.
- Pay-As-You-Go Model: This is a utility-style pricing model. You are billed only for the resources you actually consume—per hour or even per second.
- Redundancy and High Availability: Cloud providers build their infrastructure across multiple geographic regions and data centers. You can design your application to run simultaneously across multiple locations. If one data center fails, your application automatically fails over to a healthy one, resulting in zero downtime.
The "as-a-Service" Models
Cloud hosting is typically categorized into three main service models:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): The provider gives you the raw building blocks: virtual servers, storage, and networking. You are responsible for installing and managing everything else. Example: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): The provider manages the underlying infrastructure and operating system. You simply upload and manage your application code. Example: Heroku, Google App Engine.
SaaS (Software as a Service): You consume a finished software product delivered over the internet. The entire stack is managed by the provider who may use subscription billing software to manage invoicing (e.g., via AP automation for Intacct) and automate reporting. Example: Google Workspace, Salesforce(see how to set up a Salesforce developer account here).
The Unmatched Advantages of Cloud Hosting
- Virtually Infinite Scalability (Elasticity): This is the cloud's killer feature. Whether you need to handle a viral traffic spike or the rush of a Black Friday sale, cloud hosting can scale on demand, often automatically.
- Unparalleled Reliability and Uptime: Due to its distributed nature, cloud hosting offers extremely high levels of availability. The failure of a single piece of hardware does not impact your service.
- Cost-Efficiency for Variable Loads: The pay-as-you-go model eliminates the need to pay for a powerful server to handle peak traffic that only occurs 1% of the time.
- Ultimate Control and Customization: You have deep, granular control over every aspect of your environment. For teams with DevOps expertise, this level of control is invaluable.
- Global Reach: Major cloud providers have data centers worldwide, allowing you to deploy your application closer to your end-users to reduce latency.
The Significant Disadvantages of Cloud Hosting
- Complexity and Required Expertise: Properly configuring and managing a cloud environment requires specialized knowledge in cloud architecture, networking, and security.
- Unpredictable Costs and "Bill Shock": If you're not carefully monitoring your usage, costs can spiral out of control. A traffic spike or misconfigured script can lead to a shockingly large bill.
- The Shared Responsibility Model: The cloud provider is responsible for the security of the cloud (the physical hardware). However, you are responsible for security in the cloud, including securing your OS, managing access, and encrypting data.
- Performance Variability: In a public cloud, you share hardware with other customers. While rare, another customer's high-demand workload (the "noisy neighbor" effect) can temporarily impact your performance in the absence of workload automation software.
Build your Website in seconds
- What is your brand name?
- What kind of business you are in?
- What kind of products or services you offer?
Blurring the Lines: The Rise of Managed Cloud Hosting

The market has recognized the chasm between the simplicity of managed hosting and the power of the cloud. This has given rise to a hybrid solution: Managed Cloud Hosting.
In this model, a provider builds a user-friendly management layer on top of the raw infrastructure from a major cloud provider like AWS or Google Cloud.
- How it Works: You choose your underlying cloud provider through the managed host's simple interface. They handle the complex backend tasks of provisioning the server, securing the environment, and managing updates.
- Who it's for: This is the ideal solution for businesses that want the scalability of the cloud without needing to hire an expensive in-house DevOps team. You get the power of AWS without needing to become an AWS expert Still, taking an AWS course can help you better understand how your managed host leverages AWS services for performance and reliability..
Head-to-Head Comparison: Managed Hosting vs. Cloud Hosting
|
Factor |
Managed Hosting |
Cloud Hosting (IaaS) |
|
Management |
Provider handles everything. Proactive monitoring,
updates, security, and support are included. |
User manages almost everything. You are responsible for
OS, security, patching, and configuration. |
|
Performance |
Optimized for specific applications but ultimately
limited by a single server's resources. |
Scales dynamically across a distributed network.
Performance is highly configurable. |
|
Scalability |
Structured plan upgrades. Requires manual intervention
or provider assistance. Not instantaneous. |
Instantaneous and often automated (elastic). Scale up
or down in minutes. |
|
Reliability |
High, but often dependent on a single server. A
hardware failure can cause downtime. |
Extremely high due to built-in redundancy across
multiple servers and data centers. |
|
Customization |
Restricted. The provider controls the environment to
ensure stability. No root access. |
Highly customizable. Full root access to configure the
server environment exactly as needed. |
|
Security |
Fully provider-managed. A team of experts proactively
secures your server. |
Shared Responsibility. You must configure firewalls,
manage access, and secure your data and applications. |
|
Cost Structure |
Predictable. Fixed monthly or annual fee, making
budgeting easy. |
Usage-based. Can be highly variable and fluctuate with
traffic and resource consumption. |
|
Required Expertise |
Minimal. Ideal for non-technical users and businesses
without an IT team. |
High. Requires significant expertise in system
administration, networking, and cloud architecture. |
Making the Right Choice: Which Hosting Is for You?
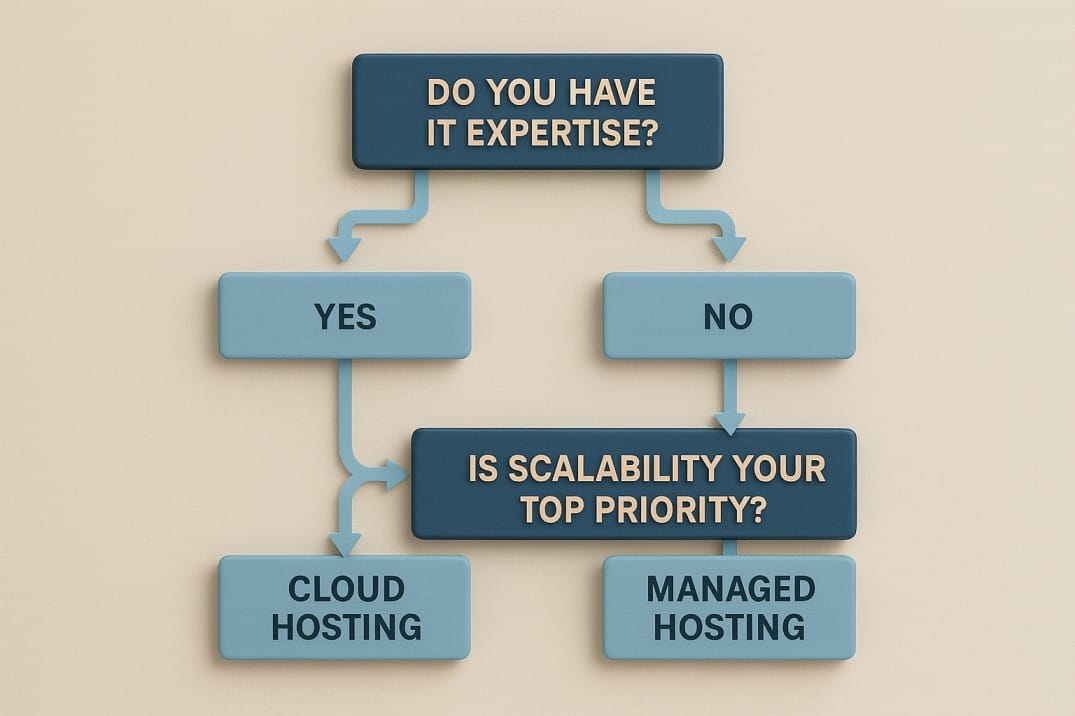
The best hosting solution is the one that aligns with your business's technical resources, budget model, and growth ambitions. Ask yourself these critical questions:
1. What is the level of technical expertise on my team?
- Choose Managed Hosting if: You have no dedicated IT staff or your tech team is focused on product development. You value convenience and want to completely offload server management.
- Choose Cloud Hosting if: You have a skilled DevOps team in-house. Your team is comfortable with the command line, understands network security, and is prepared to manage the entire infrastructure stack.
2. What are my anticipated traffic patterns and growth plans?
- Choose Managed Hosting if: Your website has relatively stable, predictable traffic and you anticipate steady, linear growth.
- Choose Cloud Hosting if: You expect explosive growth, viral traffic spikes, or highly variable usage patterns that require the ability to handle a sudden influx of traffic without crashing.
3. What is my budget model and tolerance for variability?
- Choose Managed Hosting if: You operate on a fixed budget and need predictable operational expenses.
- Choose Cloud Hosting if: You are comfortable with a utility-based billing model and have expense management systems in place to monitor costs.
4. How much control and customization do I truly need?
- Choose Managed Hosting if: You are using a standard application like WordPress and don't need to install custom software or make deep changes to the server environment.
- Choose Cloud Hosting if: You are building a custom application with specific dependencies or require granular control over networking and security for compliance reasons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between cloud hosting and managed cloud hosting?
A: Cloud hosting (like AWS EC2) gives you raw, unmanaged infrastructure. Managed cloud hosting adds a service layer on top, where a provider handles all the management, security, and optimization for you. It's the convenience of managed hosting with the power of the cloud.
Q: What is a VPS, and how does it relate to these options?
A: A VPS (Virtual Private Server) is where a physical server is partitioned into several virtual servers. A VPS can be either unmanaged (similar to a small cloud instance) or managed. It's often a middle ground between basic shared hosting and a full dedicated or cloud solution.
Q: Can I migrate from managed hosting to cloud hosting later?
A: Absolutely. Migration is a common step for growing businesses, but it is a complex process that requires careful planning to migrate data, reconfigure applications, and manage DNS changes to minimize downtime.
Q: Is cloud hosting always more performant than managed hosting?
A: Not necessarily. A high-end, finely-tuned managed dedicated server can easily outperform a small, poorly configured cloud instance. The cloud's performance advantage lies in its ability to scale resources to maintain performance under heavy load.
Conclusion: Convenience vs. Control
The choice between managed and cloud hosting is a strategic business decision that boils down to a fundamental trade-off: convenience versus control.
- Managed hosting is about simplicity and peace of mind. It's a fully supported solution that empowers you to focus on your core business, secure in the knowledge that experts are keeping your online presence fast and stable.
- Cloud hosting is about flexibility and power. It provides an unparalleled toolkit for building highly available applications that can grow on demand. It's ideal for tech-savvy organizations with the in-house expertise to harness its full potential.
At CodeDesign.ai, we urge our clients to conduct an honest assessment of their business's internal resources, budget, and long-term growth trajectory. The right hosting solution isn't just a technical detail; it's a strategic asset that powers your business today and provides a solid foundation for your ambitions tomorrow. Choosing the right partner to help you build on that foundation is the next critical step.
References